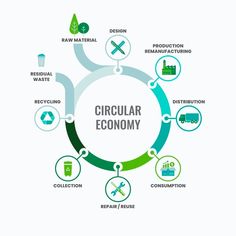
The circular economy offers a revolutionary approach to tackling the economic and environmental challenges faced by many developing countries. Unlike the linear model of “extract, produce, discard,” the circular economy emphasizes the reuse, repair, and recycling of materials to create sustainable and inclusive growth. In this article, we explore how this transition can transform local economies while preserving natural resources for future generations.
What is the Circular Economy?
- Define the circular economy.
- Differences with the linear model.
- Why is it relevant for developing countries?
The Economic and Social Benefits of the Circular Economy
- Reduction of costs for businesses through the recycling of raw materials.
- Job creation in recycling and repair sectors.
- Development of local skills and empowerment of communities.
Case Studies in Developing Countries
- Example 1: Plastic waste management in Kenya.
- Example 2: The smartphone repair industry in India.
- Example 3: Agricultural waste valorization in Brazil.
Challenges and Barriers to Implementing
- Lack of awareness and infrastructure.
- Dependence on traditional economic models.
- Need for public policies to encourage circular innovation.
Solutions for a Successful Transition to the Circular economy developing countries
- Investments in recycling infrastructure.
- Public-private partnerships to develop circular ecosystems.
- Raising awareness among consumers and local businesses.
The circular economy represents a crucial pathway for developing countries, allowing them to integrate sustainability into their economic models while reducing environmental pressures. Although numerous challenges remain, such as the lack of infrastructure and awareness, the potential benefits are undeniable. By promoting reuse, recycling, and waste reduction, these nations can stimulate economic growth while creating jobs and improving the quality of life for their populations. To succeed in this transition, it is essential to adopt suitable public policies and strengthen partnerships between the private sector, governments, and local communities. Thus, the circular economy could become a driver of sustainable and inclusive transformation for developing countries.